Next.js + PWA 오프라인 캐싱에 대하여 feat: serwist/next
Next.js PWA 오프라인 전략: 네비게이션과 데이터, 캐시 이야기
PWA(Progressive Web App)는 웹 기술(HTML, CSS, JavaScript 등)을 사용하여 개발되었지만, 설치형 네이티브 앱과 유사한 사용자 경험을 제공하는 웹 앱입니다. 웹사이트의 접근성과 네이티브 앱의 기능성을 결합한 형태라고 할 수 있습니다.
최근 온라인 & 오프라인 하이브리드 환경에서 동작하는 POS 웹앱을 Next.js로 개발하고 있다.. 들어는 봤나 PWA!

요구사항 : "이륙하면 인터넷이 끊긴다. 그래도 앱은 정상 작동해야 한다."
Next.js 15 + App Router에 output: 'export'로 정적 배포를 선택했고, PWA 기능은 @serwist/next로 구현하기로 했다. 문제는 오프라인 환경에서 두 가지를 동시에 해결해야 한다는 것이었다. ( 해본 적 없는데, 해야함^^)
- 네비게이션 캐싱: 한 번도 방문하지 않은 페이지도 오프라인에서 열려야 한다.
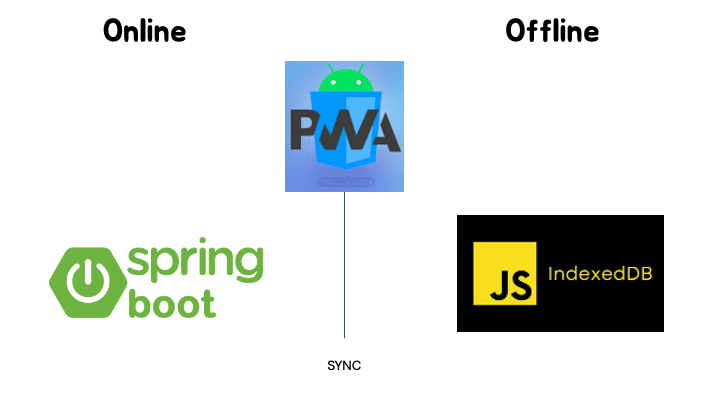
- 데이터 캐싱: API 응답을 로컬(spring boot)에 저장하고, 오프라인에서는 로컬 DB를 바라봐야 한다
- 그리고 온라인 상태를 복귀하면 Indexeddb는 스프링부트에 싱크한다.
이 두 가지 문제를 어떻게 해결했는지 공유한다.
기술 스택 웹앱 :안드로이드 네이티브 > web app (pwa) [ nextjs 15 + serwist ] 온라인 백엔드 : java spring boot 오프라인 백엔드 (spring boot 와 sync) : indexedDB + Dexie
1. 네비게이션 캐싱: Stale HTML
문제의 발견
첫 번째 요구사항은 이렇다.
승무원이 로그인 후 즉시 이륙해도,
/sales나/inventory페이지에 접근할 수 있어야 한다.
가장 단순한 해결책은 Service Worker의 precacheEntries에 모든 페이지 HTML을 등록하는 것처럼 보였다.
// ❌ 나쁜 예시
const serwist = new Serwist({
precacheEntries: [
...(self.__SW_MANIFEST || []),
{ url: '/', revision: 'v1' },
{ url: '/sales', revision: 'v1' },
{ url: '/inventory', revision: 'v1' },
],
});이 방식은 미방문 페이지를 오프라인에서 열 수 있게 해줬지만, 치명적인 문제가 생김
Stale HTML 문제
Next.js는 빌드 시 JS/CSS 파일명에 해시를 붙인다. main.a1b2c3.js 같은 형태
- v1 배포: 사용자가 앱을 설치합니다. Service Worker는
/sales(v1 HTML)와main.a1b2c3.js(v1 JS)를 precache에 저장합니다. - v2 배포: 코드를 수정하고 재배포합니다. 새 Service Worker는
main.d4e5f6.js(v2 JS)를 precache에 저장하고, v1 JS는 삭제됩니다. - 오프라인 접속: 사용자가 오프라인 상태로
/sales에 접근합니다. - 💥 UI 깨짐: Service Worker는 캐시된 v1 HTML을 제공하는데, 이 HTML이 찾는
main.a1b2c3.js는 이미 삭제된 상태입니다. 결국 스타일과 스크립트가 로드되지 않아 화면이 완전히 깨집니다.
해결책: Runtime Cache Warming
두 가지 전략을 조합한다.
1. HTML은 Runtime Caching으로 처리
precache에서 제외하고, NetworkFirst 전략을 사용하는 런타임 캐시로 관리합니다.
2. activate 이벤트에서 캐시 예열
Service Worker가 활성화되는 시점에 오프라인에 필요한 모든 페이지를 미리 fetch하여 런타임 캐시를 "예열(warm up)"합니다.
// app/sw.ts
import { defaultCache } from '@serwist/next/worker';
import { Serwist, NetworkFirst, ExpirationPlugin } from 'serwist';
declare global {
interface WorkerGlobalScope extends SerwistGlobalConfig {
__SW_MANIFEST: (PrecacheEntry | string)[] | undefined;
}
}
declare const self: ServiceWorkerGlobalScope;
// 오프라인에 필수적인 모든 페이지
const CRITICAL_PAGES = [
'/',
'/login',
'/sales',
'/inventory',
'/settings',
];
const serwist = new Serwist({
// 정적 리소스(JS/CSS)만 precache
precacheEntries: self.__SW_MANIFEST,
skipWaiting: true,
clientsClaim: true,
navigationPreload: true,
runtimeCaching: [
...defaultCache,
{
// 페이지 네비게이션은 NetworkFirst 전략
matcher: ({ request }) => request.destination === 'document',
handler: new NetworkFirst({
cacheName: 'pages-cache',
plugins: [
new ExpirationPlugin({
maxEntries: 50,
maxAgeSeconds: 30 * 24 * 60 * 60, // 30일
}),
],
}),
},
],
fallbacks: {
entries: [
{
url: '/~offline',
matcher({ request }) {
return request.destination === 'document';
},
},
],
},
});
// ⭐️ 핵심: activate 시 캐시 예열
self.addEventListener('activate', (event) => {
event.waitUntil(
(async () => {
await self.clients.claim();
if (navigator.onLine) {
const cache = await caches.open('pages-cache');
await Promise.allSettled(
CRITICAL_PAGES.map(async (url) => {
try {
const response = await fetch(url);
if (response.ok) {
await cache.put(url, response);
}
} catch (error) {
console.warn(`Failed to prefetch ${url}:`, error);
}
})
);
}
})()
);
});
serwist.addEventListeners();이 방식으로 두 가지 문제를 동시에 해결한 것 같다.
- Stale HTML 방지: 페이지는 항상 최신 JS/CSS와 함께 캐시
- 미방문 페이지 지원: activate 시점에 모든 중요 페이지가 자동으로 캐시
2. 데이터 캐싱: Service Layer로 복잡도 숨기기
두 번째 문제는 API 데이터!
온라인에서는 Spring Boot API를, 오프라인에서는 IndexedDB를 바라봐야 했다.
안티패턴: 컴포넌트에서 분기
가장 직관적이지만 최악의 방법은 UI 컴포넌트 내부에서 navigator.onLine을 체크하는 것입니다.
// ❌ 나쁜 예시
function ItemList() {
const { data } = useQuery({
queryFn: () => {
if (navigator.onLine) {
return apiClient.get('/api/items'); // 온라인
} else {
return db.items.toArray(); // 오프라인
}
},
});
}이 방식은 모든 컴포넌트에 온/오프라인 로직이 중복되고, 테스트와 유지보수가 어려워짐.
해결책: Data Service 추상화
모든 분기 로직을 별도의 서비스 계층으로 분리.
1. IndexedDB 스키마 정의 (Dexie.js)
// lib/db.ts
import Dexie, { type EntityTable } from 'dexie';
export interface Product {
id: string;
name: string;
price: number;
stock: number;
updatedAt: number;
}
export interface Sale {
id?: number;
productId: string;
quantity: number;
totalPrice: number;
timestamp: number;
synced: boolean; // 서버 동기화 여부
}
class AircafeDB extends Dexie {
products!: EntityTable<Product, 'id'>;
sales!: EntityTable<Sale, 'id'>;
constructor() {
super('aircafe-db');
this.version(1).stores({
products: '&id, name, updatedAt',
sales: '++id, productId, timestamp, synced',
});
}
}
export const db = new AircafeDB();2. Data Service 계층
// lib/dataService.ts
import { apiClient } from './apiClient';
import { db, type Product } from './db';
// 온라인: API 호출 + IndexedDB 동기화
async function fetchProductsFromServer() {
const { data } = await apiClient.get<Product[]>('/api/products');
// 백그라운드 동기화 (UI는 기다리지 않음)
db.transaction('rw', db.products, async () => {
await db.products.clear();
await db.products.bulkPut(data);
}).catch(err => console.error('DB Sync Failed:', err));
return data;
}
// 오프라인: IndexedDB 조회
async function fetchProductsFromDB() {
return db.products.orderBy('name').toArray();
}
// ⭐️ UI가 호출할 단일 함수
export const getProducts = () => {
return navigator.onLine
? fetchProductsFromServer()
: fetchProductsFromDB();
};
// 판매 등록 (오프라인 우선)
export const createSale = async (productId: string, quantity: number) => {
const product = await db.products.get(productId);
if (!product) throw new Error('Product not found');
const sale = {
productId,
quantity,
totalPrice: product.price * quantity,
timestamp: Date.now(),
synced: false,
};
// 로컬에 먼저 저장
await db.sales.add(sale);
// 재고 감소 (낙관적 업데이트)
await db.products.update(productId, {
stock: product.stock - quantity,
updatedAt: Date.now(),
});
// 온라인이면 즉시 서버 동기화 시도
if (navigator.onLine) {
try {
await apiClient.post('/api/sales', sale);
await db.sales.update(sale.id!, { synced: true });
} catch {
// 실패해도 로컬에는 저장됨 (나중에 동기화)
}
}
return sale;
};3. UI 컴포넌트 (React Query)
이제 컴포넌트는 온라인/오프라인을 전혀 신경 쓰지 않는다.
// app/pos/page.tsx
'use client';
import { useQuery, useMutation } from '@tanstack/react-query';
import { getProducts, createSale } from '@/lib/dataService';
export default function POSPage() {
const { data: products } = useQuery({
queryKey: ['products'],
queryFn: getProducts, // ⭐️ 분기 로직 완전히 숨김
networkMode: 'offlineFirst',
});
const saleMutation = useMutation({
mutationFn: ({ productId, quantity }) =>
createSale(productId, quantity),
});
return (
<div>
{products?.map(product => (
<ProductCard
key={product.id}
product={product}
onSale={(qty) =>
saleMutation.mutate({ productId: product.id, quantity: qty })
}
/>
))}
</div>
);
}추가: 동기화 엔진
오프라인에서 발생한 변경사항은 온라인 복구 시 자동으로 동기화되어야 함.
// lib/syncEngine.ts
import { db } from './db';
import { apiClient } from './apiClient';
class SyncEngine {
async syncPendingSales() {
const unsyncedSales = await db.sales
.where('synced')
.equals(false)
.toArray();
for (const sale of unsyncedSales) {
try {
await apiClient.post('/api/sales', sale);
await db.sales.update(sale.id!, { synced: true });
} catch (error) {
console.error('Sync failed for sale:', sale.id, error);
}
}
}
startAutoSync() {
window.addEventListener('online', () => {
this.syncPendingSales();
});
// 30초마다 자동 동기화
if (navigator.onLine) {
setInterval(() => this.syncPendingSales(), 30000);
}
}
}
export const syncEngine = new SyncEngine();마무리
Next.js PWA에서 오프라인 기능을 구현하며 배운 것들:
- HTML을 precache하지 말자: Stale HTML 문제를 피하려면 NetworkFirst + Cache Warming을 사용해보자.
- *Service Layer 추상화: 온/오프라인 분기를 UI에서 분리하면 코드가 훨씬 깔끔해짐
- IndexedDB는 필수!: Service Worker는 네비게이션, IndexedDB는 데이터로 역할을 명확히 분리.
기내 환경처럼 불안정한 네트워크에서 동작하는 앱을 만들 때, 이 패턴을 참고해보길 바란다. 분명 언젠가 어이없이 이런 일을 하게 될 일이 생긴다.
그 땐 이 블로그를 보라.
결론
세상에 안되는 건 없다. 아무튼 인간이 만들어 낸 것이기에 겁먹지말고 도전해보자.
nextjs + serwist
dfdfffffff